Cervical cancer Following quite a while of uplifting news in the battle against cervical disease — set apart by many years of consistent decreases in cases and passings — another report recommends that a few ladies are overall abandoned.
On account of early location and therapy, paces of cervical disease have plunged by the greater part throughout the course of recent years. Rates are falling quickest among ladies in their mid 20s, the original to profit from HPV immunizations, which were supported in 2006.
HPV, the human papillomavirus, causes six sorts of malignant growth, including cervical disease.
Among ladies matured 20 to 24, cervical malignant growth rate dropped by 65% from 2012 to 2019, as indicated by a report set Wednesday free from the American Disease Society.
Cervical cancer
“Cervical disease is quite possibly of the best-figured out malignant growth,” said Dr. Nicolas Wentzensen, a senior specialist in the Public Malignant growth Organization’s clinical hereditary qualities branch, who was not engaged with the new report. “We’ve gained astonishing headway and it stays an example of overcoming adversity.”
Not all ladies are profiting from that advancement, in any case.
The in general cervical disease rate among ladies of any age has quit falling.
Excessively old for HPV inoculation?
Among ladies in their 30s and mid 40s, frequency has been edging up. Finding of cervical disease among ladies ages 30 to 44 rose practically 2% every year from 2012 to 2019.
“We really want to ensure we are not disregarding that age that was excessively old for HPV immunization,” said Jennifer Spencer, an associate teacher at the Dell Clinical School at College of Texas-Austin who concentrates on populace wellbeing.
Luckily, the diseases viewed as in 30-and 40-something ladies were generally early, reparable growths, said Ahmedin Jemal, senior creator of the new report and the disease society’s senior VP for reconnaissance and wellbeing value science. Around 13,800 American ladies are determined to have cervical malignant growth every year and 4,360 bite the dust from the illness.
Specialists didn’t dig into the motivations behind why cervical malignant growth is turning out to be more normal for certain ladies, Jemal said.
However, screening rates might assume a part, said Spencer, who was not engaged with the review. Screenings permit specialists to find and eliminate precancerous injuries before they become dangerous. The greater part of ladies determined to have cervical malignant growth have either never been screened or haven’t been separated the beyond five years, as indicated by the Habitats for Infectious prevention and Anticipation.
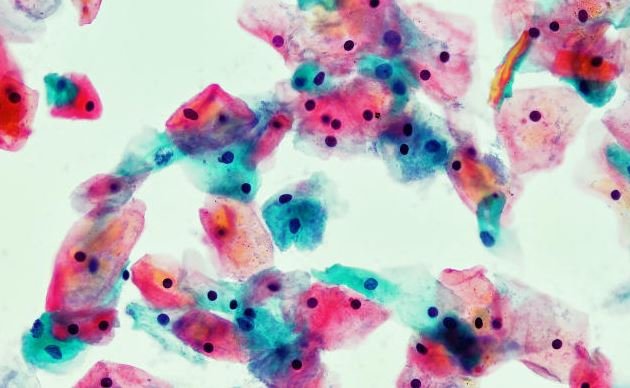
Concentrates on show that less ladies are staying aware of routine cervical disease tests.
The quantity of ladies ages 21 to 65 who have been screened by the most recent rules tumbled from 87% in 2000 to 72%, as per the Public Malignant growth Organization.
Other exploration has found that ladies ages 21 to 29 were the to the least extent liable to be modern on their screenings, with 29% being past due. Ladies were likewise bound to be bogged down on the off chance that they were nonwhite, uninsured, lived in provincial regions or distinguished as gay, lesbian or sexually unbiased, as per the review.
The U.S. Preventive Administrations Team suggests screening ladies ages 21-29 with Pap spreads — which inspect cells under a magnifying instrument — like clockwork. Ladies ages 30 to 65 can be screened either at regular intervals with a Pap smear or like clockwork with a HPV test or blend of the two tests. HPV tests can identify hereditary material from the human papilloma infection.
Spencer said conceivable low screening rates among 20-something ladies could assist with making sense of the marginally higher cervical disease rates among ladies in their 30s and mid 40s.
At the point when ladies in one of Spencer’s examinations were inquired as to why they hadn’t been screened as of late, they regularly said that they didn’t realize they should have been screened or that a wellbeing supplier hadn’t suggested it. Simply 1% ladies ages 21 to 29 said they had skipped screening since they had gotten the HPV shot.
“Obviously, more persistent instruction is required,” said Dr. Betty Suh-Burgmann, seat of gynecologic oncology for Kaiser Permanente Northern California. Her medical care framework as of now reminds ladies about screenings by postcards, letters and calls. This year, Kaiser Permanente will start messaging patients, also, she said.
Changing rules about cervical disease screening likewise may have left ladies and wellbeing suppliers befuddled, Spencer said. Until the mid 2000s, most specialists screened ladies every year. The team has refreshed its rules multiple times in the beyond twenty years, and is currently evaluating them once more.
Others say the expansion in cervical malignant growth rates among 30-and 40-something ladies isn’t really effectively made sense of.
Cervical cancers will quite often develop gradually, normally requiring 10 years or more to transform from precancers to tumors, Wentzensen said. He said there might be different elements impacting everything. For instance, he contemplates whether more ladies moving to the US haven’t been screened, putting them at higher gamble.
Also, Spencer noticed that screening is only the initial step to saving lives. Ladies with strange screening results need to go through extra testing and, if fundamental, treatment.
In a review distributed last year in the American Diary of Preventive Medication, Spencer and her partners viewed that as just 73% of ladies with strange screening results got follow-up care.
“The onus is on the medical care framework to contemplate who is escaping everyone’s notice,” Spencer said.
Cervical cancerCervical cancerCervical cancerCervical cancerCervical cancerCervical cancerCervical cancer